Treatments
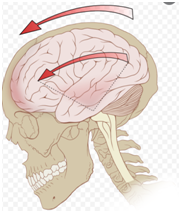
Head Injury
Head Injury Trauma is one of the leading causes of death and disability in the Indian population. It i

Head Injury Trauma is one of the leading causes of death and disability in the Indian population. It i